Liver Diseases

There is a stereotype surrounding liver disease. Help us end it.
Statistics show that liver disease is on the rise. 1 in 4 Canadians may be affected by liver disease, including everyone from newborns to older adults.
Did you know?
- There are over 100 liver diseases caused by a variety of factors including; viruses, toxins, genetics, alcohol and unknown causes.
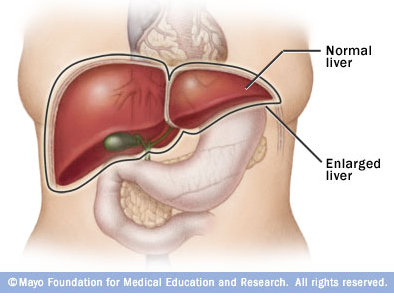
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is the most common liver disease in Canada, affecting over 7 million people.
- Biliary atresia is the leading cause of liver failure in children.
- Acetaminophen (Tylenol) overdose is the leading cause of acute liver failure
- Liver cancer is now one of the fastest rising and deadliest forms of cancer in Canada.
Learn about liver diseases and complications below.
Additional information
Hepatopulmonary Syndrome (HPS) is a condition that affects the lungs of people diagnosed with chronic liver disease. In the lungs, capillaries (small blood vessels that can be found throughout the body) play a crucial role in the oxygenation of the blood. When the liver is severely damaged, the capillaries in the lungs become dilated, affecting the absorption of oxygen by the red blood cells. As a result of the dilated capillaries, the lungs are not able to provide the body with adequate amounts of oxygen, resulting in a condition known as hypoxemia.
Low levels of oxygen in the blood have a major impact on the body. Most common symptoms of HPS include shortness of breath and difficulty breathing that is relieved when lying down. A common treatment option for HPS is supplemental oxygen. The ultimate cure for HPS is a liver transplant. Once an individual has a healthy liver, the capillaries in the lungs will revert to their original size allowing the blood in the lungs to oxygenate, eliminating associated symptoms and curing the individual of HPS.
For more information on Hepatopulmonary Syndrome (HPS) please visit hpscare.com.
Ordering Printed Materials
Our printing and shipping services for educational material is temporarily suspended. If you require online materials of the diseases listed above, please send your request by email to publication orders



